Reasons for Impotence. Erectile Dysfunction Causes.
By Elaine Waller, PharmD / Last Updated:
Reviewed by Eli Coleman, PhD
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) affects approximately 30 million adult men in the United States alone. Before advancements in medical understanding, like those found in publications indexed by PubMed, it was often believed that the etiology of reasons for impotence was primarily psychological. However, research has demonstrated that around 80% of erectile dysfunction causes stem from physical factors. Impotence arises from a complex interplay of three primary factors: physical, psychogenic, and lifestyle.
Physical Factors
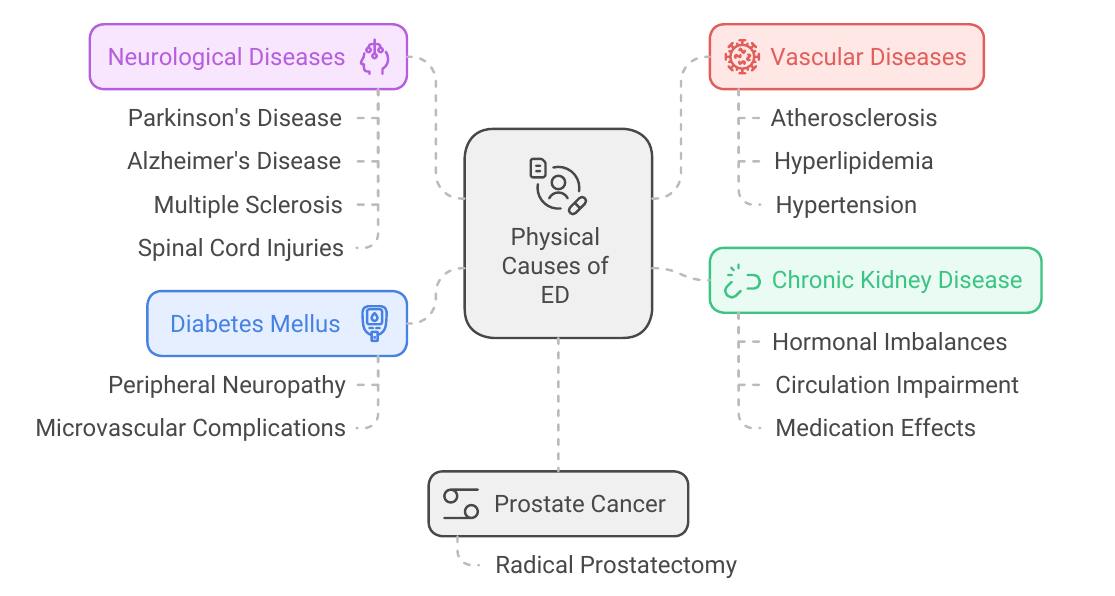
Physical factors are the most prevalent causes of ED. While ED can induce stress, anxiety, and depression, these are not the root causes. Instead, ED can be a symptom of more serious underlying medical conditions.
- Vascular Diseases: Conditions like atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol), and hypertension (high blood pressure) impact the circulatory system, including the endothelial cells lining blood vessels. These diseases restrict blood flow to various organs, including the penis, hindering the ability to achieve an erection. Vascular diseases account for at least 70% of physically-related ED cases.
- Diabetes Mellitus: This metabolic disorder can damage nerves and blood vessels, including those crucial for erectile function. The peripheral neuropathy associated with diabetes can impair nerve signaling to the penis, while microvascular complications can reduce blood flow. Approximately 35% to 50% of men with diabetes experience ED.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): CKD can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting testosterone levels and reducing libido. Additionally, CKD can impair circulation and some medications used in its management can contribute to ED.
- Neurological Diseases: The nervous system plays a vital role in the erectile process. Conditions like Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries can disrupt nerve signals required for achieving and maintaining an erection. These neurological conditions can affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which regulates sexual function.
- Prostate Cancer: While prostate cancer itself may not directly cause ED, treatments like radical prostatectomy (surgical removal of the prostate) can damage nerves and blood vessels involved in erection.
Other physical causes not directly linked to diseases include:
- Surgery (e.g., pelvic surgery)
- Injury (e.g., trauma to the perineum)
- Hormonal Imbalance (e.g., hypogonadism)
- Venuous Leak (dysfunction of the veins in the penis)
- Prescription Drugs (e.g., certain antidepressants, beta-blockers)
Psychogenic Factors
While physical factors are predominant, psychological factors can also contribute to ED, accounting for 10% to 20% of cases. These factors can be deeply rooted in a person's past experiences, including childhood trauma. A relaxed mental state is crucial for healthy sexual function.
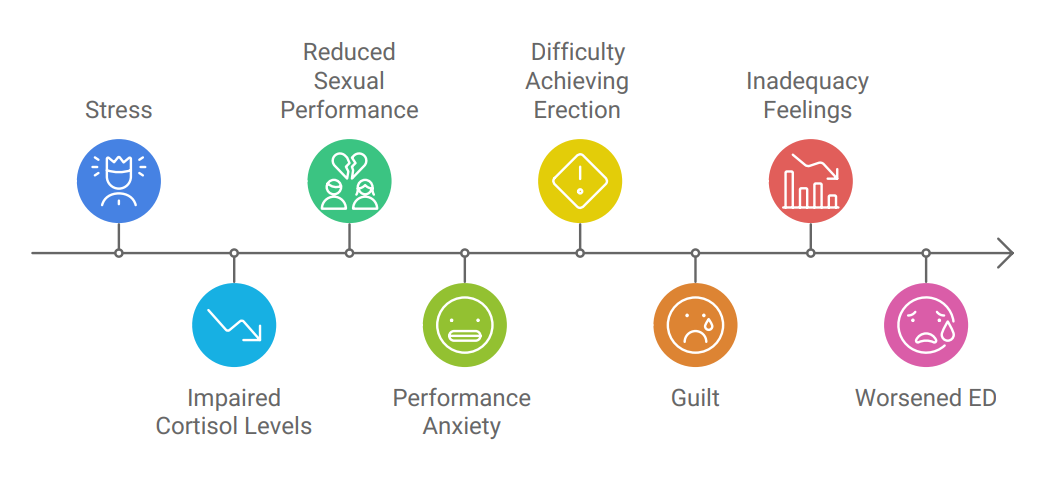
- Stress: Chronic stress from work, finances, or relationships can negatively impact cortisol levels and impair sexual performance.
- Performance Anxiety: Experiencing occasional difficulty achieving an erection can lead to anxiety about future sexual encounters, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates ED.
- Guilt: Feelings of inadequacy and guilt about not satisfying a partner can further increase anxiety and worsen ED.
- Depression: This mood disorder can affect both physical and psychological aspects of sexual health. Some antidepressants used to treat depression can also have ED as a side effect.
- Low Self-Esteem: This can stem from previous episodes of ED or other unrelated issues, leading to feelings of inadequacy and impacting sexual confidence.
- Relationship Problems: Indifference towards sexual intimacy can arise from various factors, including reduced libido, age-related changes, medication side effects, or relationship strain.
Lifestyle Factors
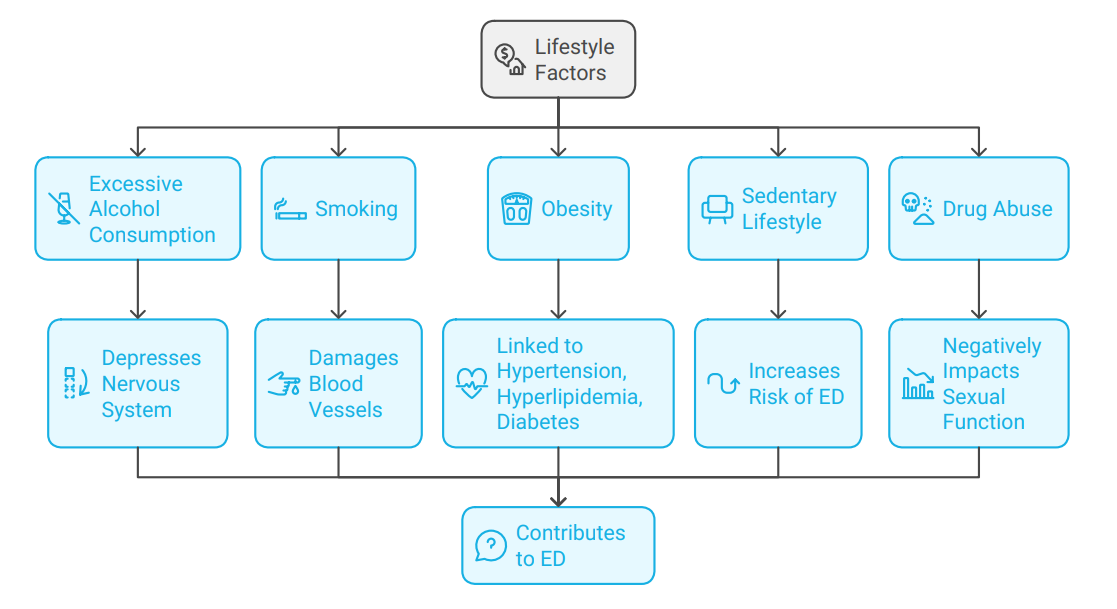
Lifestyle choices significantly influence the risk of developing ED.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can depress the nervous system and increase the likelihood of ED.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the penis, contributing to ED. It also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, a major risk factor for ED.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is linked to hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes, all of which are risk factors for ED. Adipose tissue can also produce hormones that interfere with sexual function.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of developing ED and other health problems. Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health and can help prevent ED.
- Drug Abuse: Recreational drugs like marijuana, cocaine, and ecstasy can negatively impact sexual function and contribute to ED.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, various treatment options are available to address erectile dysfunction, depending on the underlying cause and individual needs. These options can be broadly categorized into:
Medication
Several medications have been developed to effectively treat ED. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors, such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra), are commonly prescribed. These medications work by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection. Other medications, such as alprostadil, which can be injected directly into the penis or inserted as a pellet into the urethra, may be used in cases where PDE5 inhibitors are ineffective or contraindicated.
Therapy
Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, and relationship issues, can significantly contribute to ED. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and sex therapy can help individuals address these underlying psychological issues and develop coping mechanisms to improve sexual function. Therapy can also be beneficial for couples experiencing relationship difficulties that are impacting their sexual intimacy.
Lifestyle Changes
Modifying lifestyle factors can play a crucial role in managing and even reversing ED. These changes may include:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs blood flow, contributing to ED.
- Reducing alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can depress the nervous system and interfere with sexual function.
- Losing weight: Obesity is linked to various health problems, including ED. Weight loss can improve cardiovascular health and hormonal balance.
- Increasing physical activity: Regular exercise promotes blood flow and overall health, which can benefit erectile function.
- Improving diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can support cardiovascular health and improve erectile function.
Surgery
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat ED. Penile implants, which are surgically placed devices that help achieve an erection, can be an option for men who have not responded to other treatments. Vascular surgery may be considered in cases where ED is caused by a blockage in the arteries supplying blood to the penis.
Online Pharmacy: A Convenient Option for ED Treatment
The rise of online pharmacies has provided a convenient and discreet way for men to access ED treatment. These platforms offer several advantages, including:
Online Consultation
Internet pharmacies offer online consultations with licensed physicians. This allows individuals to discuss their symptoms and medical history with a doctor from the comfort of their own home, without the need for an in-person visit.
Prescription Medication
Following an online consultation, if appropriate, the online doctor can issue a prescription for ED medication. This prescription can then be filled by the online pharmacy and shipped directly to the patient's address.
Discreet Shipping
Mail-Order pharmacies typically offer discreet shipping, ensuring that the medication is packaged in a plain, unmarked box to protect patient privacy.
Order-CS and Support-Rx
E-pharmacies, such as Order-CS and Support-Rx, specialize in providing prescription medications, including ED treatments, at competitive prices. These platforms often have customer support center teams available to answer questions and assist with the ordering process.
FAQs:
- What are the reasons for erectile dysfunction?
- Erectile dysfunction (ED) can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and nerve damage; psychological factors like stress, anxiety, and depression; and lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise.
- Can erectile dysfunction be cured?
- In many cases, ED can be successfully treated and managed. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include lifestyle changes, medication, therapy, or surgery.
- Why does my erection go away so fast?
- Several factors can contribute to losing an erection quickly, including anxiety, stress, medication side effects, hormonal imbalances, and vascular problems. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause in your case.
- How to fix ED fast?
- While there are no instant "cures" for ED, certain strategies may help improve erectile function in the short term. These include reducing stress, engaging in foreplay, trying oral medications (after consulting a doctor), and ensuring adequate sleep and hydration. However, addressing the underlying cause of ED is crucial for long-term improvement.
Disclaimer:
The content on this website, including assessments and suggestions for pharmacies, is provided for general knowledge purposes only. It is not meant to replace the advice of a medical professional, nor should it be used to make decisions about your health without consulting a qualified healthcare provider.
The opinions and experiences shared on this website are those of individual users and do not represent the views of any medical or health organization. The accuracy of the content cannot be guaranteed and may not reflect the latest medical research or best practices. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any decisions about your health, and do not rely solely on the information presented on this website.
Author
Elaine Waller, PharmD

Dr. Elaine Waller has substantial experience in domestic and international regulatory affairs, and in clinical research. Vice President of Regulatory Affairs and Quality Assurance. Prior to joining Sonus Pharmaceuticals in July 2003, she was Chief Operating Officer at Radiant Research, a clinical site management organization. Dr. Waller's previous experience includes senior positions in regulatory affairs and clinical research at Hoechst Marion Roussel and Marion Merrell Dow. She began her career in academia at the University of Texas at Austin where she held teaching positions in both graduate and undergraduate pharmacy education and was Assistant Director of Clinical Research at the Drug Dynamics Institute. Dr. Waller received a B.S. in Pharmacy and a Doctor of Pharmacy from the University of Missouri - Kansas City, and an M.B.A. from Rockhurst University.



